Ingest Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) data into SCS
A Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is a list of all the components, libraries, and other dependencies used in a software application. While Harness SCS enables you to generate SBOMs, it also supports the ingestion of SBOMs in JSON, SPDX or CycloneDX formats, generated by any third-party tool.
Configure the SBOM Orchestration step in SCS to seamlessly ingest SBOM. In this example, we will generate an SBOM using the Trivy CLI in a CI Run step, and then ingest it using the SBOM Orchestration step.
You can ingest SBOM for both container and non-container images.
Configure your pipeline to ingest SBOM
-
In your Harness pipeline, Navigate to the stage where you want to ingest the SBOM, and select the Overview tab.
-
In Shared Paths, enter a path to a location where your SBOM can be stored on the build machine, such as
/shared/customer_artifacts.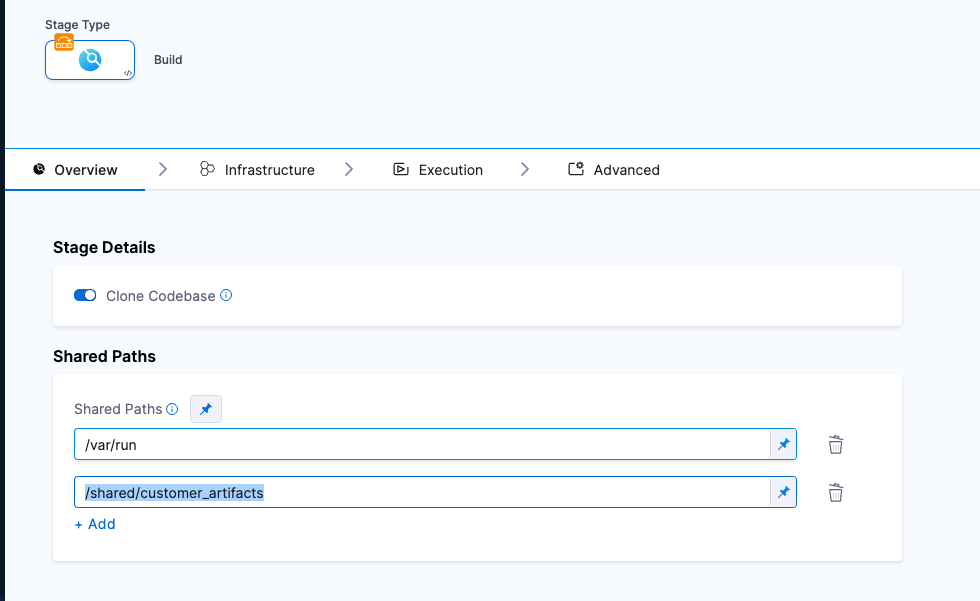
-
Add a step to your stage that generates an SBOM, such as a Run, Plugin, or GitHub Action step.
For example, this Run step uses Aqua Trivy to generate an SBOM.
trivy image \
--format spdx-json \
--output /shared/customer_artifacts/result.spdx.json \
ubuntu:22.04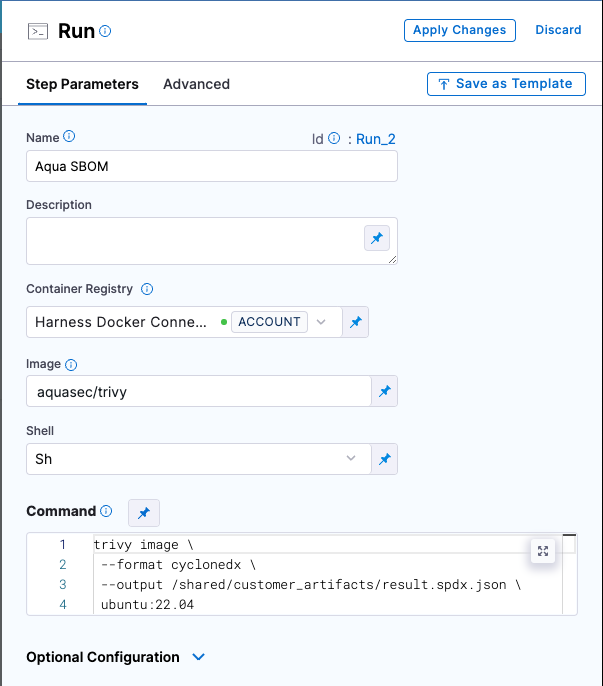
-
If your SBOM tool can't output directly to your Shared Path, then add commands or a Run step to copy the SBOM into the directory specified in Shared Paths.
SBOM Orchestration step in deploy stage can only be used in the Containerized Step Groups
Container Images
Follow the instructions below to ingest the SBOM for container images:
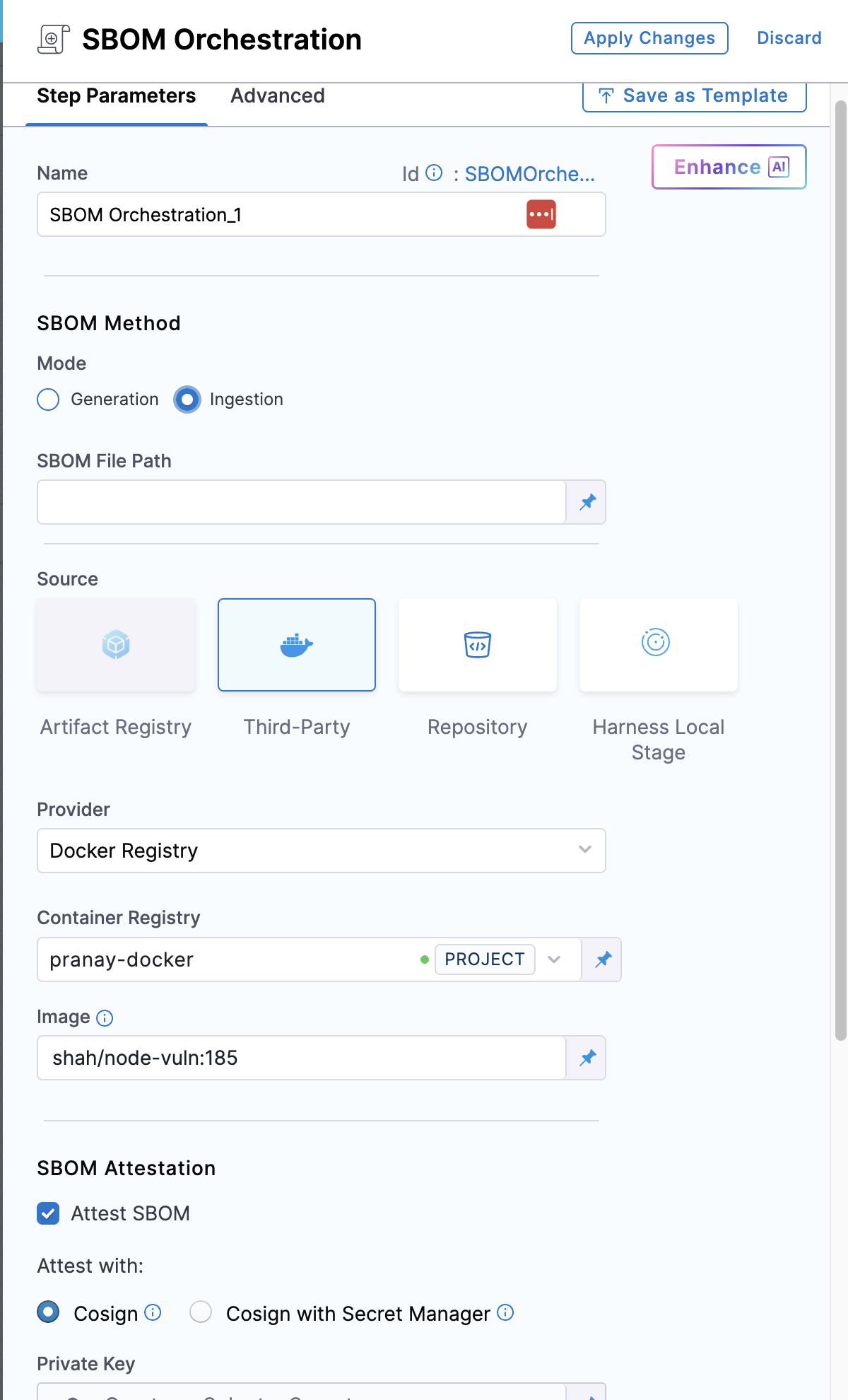
- Step Mode: Set the step mode to Ingestion.
- SBOM File Path: enter the path to the SBOM file generated by your SBOM tool.
- Source: Set the source, which can be Docker Registry, ECR, GCR, ACR or Repository. Depending on your selection, a unique set of fields will appear, each specific to the source you've chosen. Address these fields as required, this is similar to configuring the source in SBOM Orchestration step. For more details of what each field entails, please refer to the documentation on SBOM Orchestration. If you are using Docker Registry, you can follow along.
- Image: Enter the name of your image with tag or digest, such as
my-docker-org/repo-name:tagormy-docker-org/repo-name@sha256:digest.
You can securely sign the artifacts using Cosign or Cosign with Secret Manager
- Cosign
- Cosign with Secret Manager
To perform Artifact Signing with Cosign selected, you need a key pair. Follow the instructions below to generate the key pair. To perform the attestation process, you need to input the private key and password. Use Cosign to generate the keys in the ecdsa-p256 format. Here’s how to generate them:Generate key pairs using Cosign for Artifact Signing
cosign generate-key-pair to generate the key pairs..key file and a public key as a .pub file. To securely store these files, use Harness file secret.
- Private Key: Input your Private key from the Harness file secret.
- Password: Input your Password for the Private key from the Harness file secret.
In this mode, you can pass your Cosign keys using a Secret Manager. Currently, SCS supports only the HashiCorp Vault secret manager. You can connect your Vault with Harness using the Harness HashiCorp Vault connector. Here are the key points to consider when connecting your Vault:
Ensure your Harness delegate is version 25.07.86401 or higher. Upgrade if you're using an older version to enable this feature.
- Enable the Transit Secrets Engine on your HashiCorp Vault. This is essential for key management and cryptographic operations.
- Configure your HashiCorp Vault connector using the following authentication methods AppRole, Token, JWT Auth or Vault Agent.
- Create a Cosign key pair of type
ecdsa-p256,rsa-2048, orrsa-4096in the Transit Secrets Engine. You can do this in two ways:- CLI: Run the command:
vault write -f <transit_name>/<key_name> type=ecdsa-p256 - Vault UI: Create the key pair directly from the Vault interface.
- CLI: Run the command:
- Ensure the Vault token generated has the required policy applied for Cosign to perform attestation operations.
Configure the following fields in the step to perform the attestation
- Connector: Select the HashiCorp Vault connector.
- Key: Enter the path to the Transit Secrets Engine in your HashiCorp Vault where the keys are stored.
Vault is supported only for Kubernetes and VM infrastructure.
Non-Container Images:
Artifacts aren’t limited to container images. With the SBOM Orchestration step, you can also ingest SBOMs for non-container artifacts, with each artifact uniquely identified by its digest (SHA).
The following are the non-container artifact types are supported:
- Helm (
.tgz) - YAML manifest (
.yaml,.yml) - Jar (
.jar) - War (
.war) - Artifacts that are not listed above will be considered as
Unknowntype.
Follow the instructions below to ingest the SBOM for non-container images:
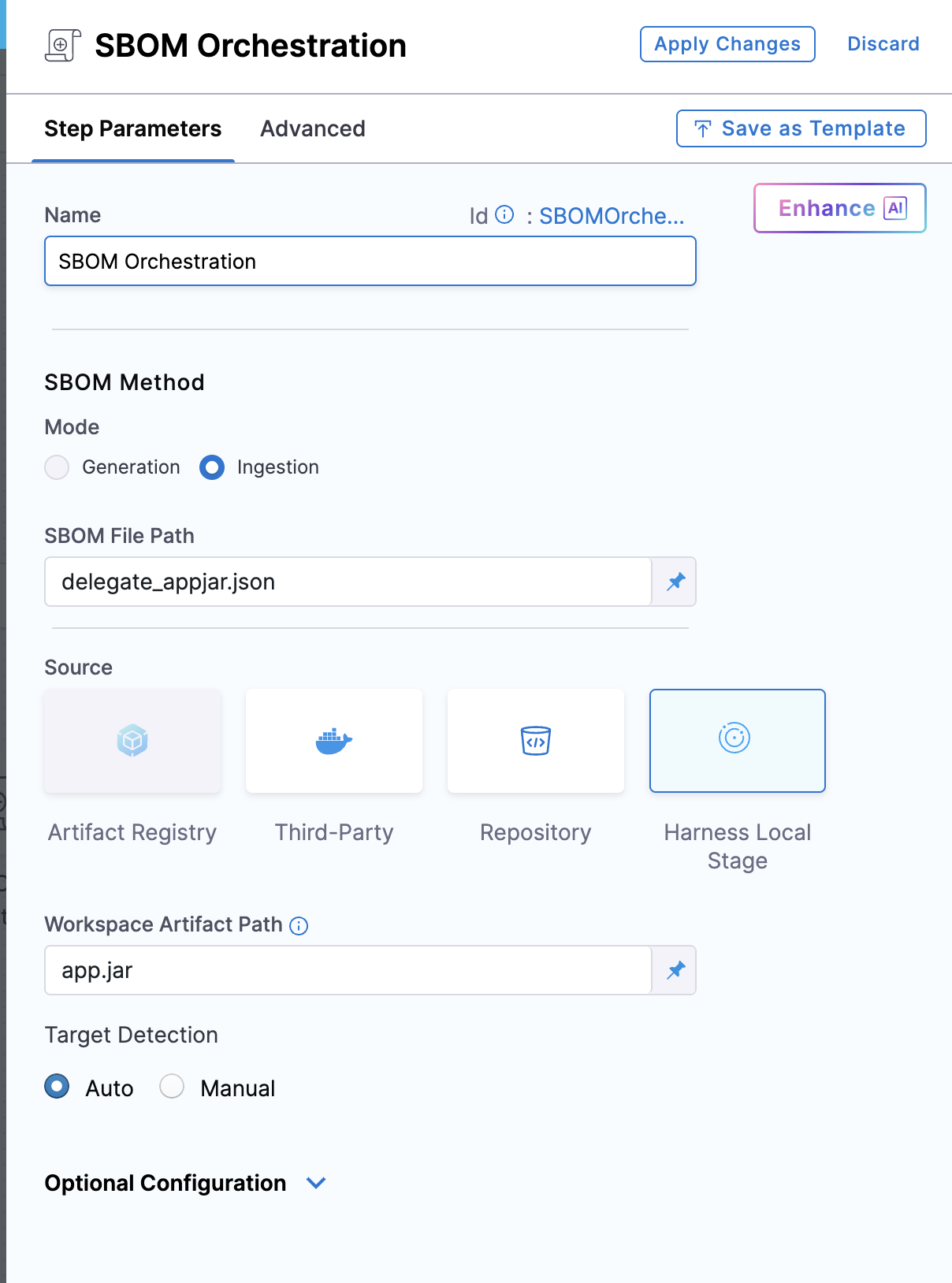
Name: Provide a name for the sbom step.
SBOM File Path: Enter the path to the SBOM file generated by the SBOM tool.
Artifact Source: Select the Harness Local Stage as the source of the artifact.
Workspace Artifact Path: Provide the exact path to the artifact within the workspace. Ensure that you run a custom step to pull the artifact into the workspace directory.
Target Detection: Choose between Auto and Manual.
Auto (default): Automatically sets the artifact name from the provided path.
Manual: Allows you to manually specify the artifact name and version.
SBOM ingestion for non-container artifacts does not currently support attestation, and the SBOM policy enforcement step.
Run the pipeline
When the pipeline runs, the SBOM Orchestration step performs the following actions:
- Ingests the SBOM to SCS module.
- Specifically for Containers:
- Generates and signs an attestation using the provided private key and password.
- Stores the SBOM in Harness and uploads the
.attfile to your container registry.
SBOMs for both Containers and Code Repositories are accessible in the Artifacts view. Additionally, you can locate the SBOM for any artifact on the Supply Chain tab within the Execution Details page in Harness. For detailed insights, please refer to the view pipeline execution results documentation.