ChaosHub Scopes
ChaosHub Scopes
Harness Chaos supports Chaos Hubs at different organizational scopes, allowing you to manage and share chaos experiments and faults at various levels within your organization. This hierarchical approach provides flexibility in organizing and controlling access to your chaos engineering resources.
ChaosHub Scopes are part of the enhanced New Chaos Studio experience. If you're an existing customer and want access to new features, contact your Harness support representative. For more details, see New Chaos Studio Features.
Different available Scopes
Chaos Hubs can be configured at three different scopes:
1. Account Level ChaosHub
Scope: Available across all projects within a specific Harness account
Access: Accessible to all users within the account (subject to RBAC permissions)
Use Cases:
- Cross-project standardized experiments
- Common infrastructure chaos scenarios
- Shared best practices across teams
- Account-wide chaos engineering templates
Benefits:
- Standardization: Promote consistent chaos engineering practices across projects
- Resource Sharing: Avoid duplication of common experiments across projects
- Centralized Management: Single point of control for account-wide chaos scenarios
- Knowledge Sharing: Teams can learn from and build upon each other's experiments
2. Organization Level ChaosHub
Scope: Available across all accounts within a Harness organization
Access: Accessible to all users across the entire organization (subject to RBAC permissions)
Use Cases:
- Enterprise-wide chaos engineering standards
- Global infrastructure resilience testing
- Cross-account shared experiments
- Corporate governance and compliance scenarios
Benefits:
- Enterprise Governance: Maintain organization-wide chaos engineering standards
- Maximum Reusability: Share experiments across all accounts and projects
- Global Visibility: Centralized view of all chaos engineering activities
- Compliance: Ensure consistent security and compliance practices
3. Project Level ChaosHub
Scope: Limited to a specific project within an organization
Access: Available only to users within that particular project
Use Cases:
- Project-specific experiments and faults
- Team-focused chaos engineering scenarios
- Isolated testing environments
- Custom experiments tailored to specific applications or services
Benefits:
- Isolation: Experiments are contained within the project boundary
- Focused Management: Easier to manage project-specific chaos scenarios
- Team Autonomy: Project teams can maintain their own chaos experiments
- Reduced Complexity: Smaller scope makes it easier to organize and find relevant experiments
Scope Hierarchy and Inheritance
The Chaos Hub scopes follow a hierarchical structure:
Account Level (Global)
↓
Organization Level (Cross-project)
↓
Project Level (Team-specific)
Choosing the Right Scope
Consider the following factors when deciding on the appropriate scope for your Chaos Hub:
| Factor | Account Level | Organization Level | Project Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audience | Multiple teams in account | Enterprise-wide | Single team/project |
| Maintenance | Account admins | Organization admins | Team responsibility |
| Standardization | Account-wide | Enterprise-wide | Team-specific |
| Governance | Moderate | High | Minimal |
| Reusability | Moderate | Maximum | Limited |
Managing ChaosHub Scopes
Setting Up Scoped ChaosHub
-
Navigate to ChaosHubs: Go to the Chaos Engineering module and choose the scope you want to create a ChaosHub for.
-
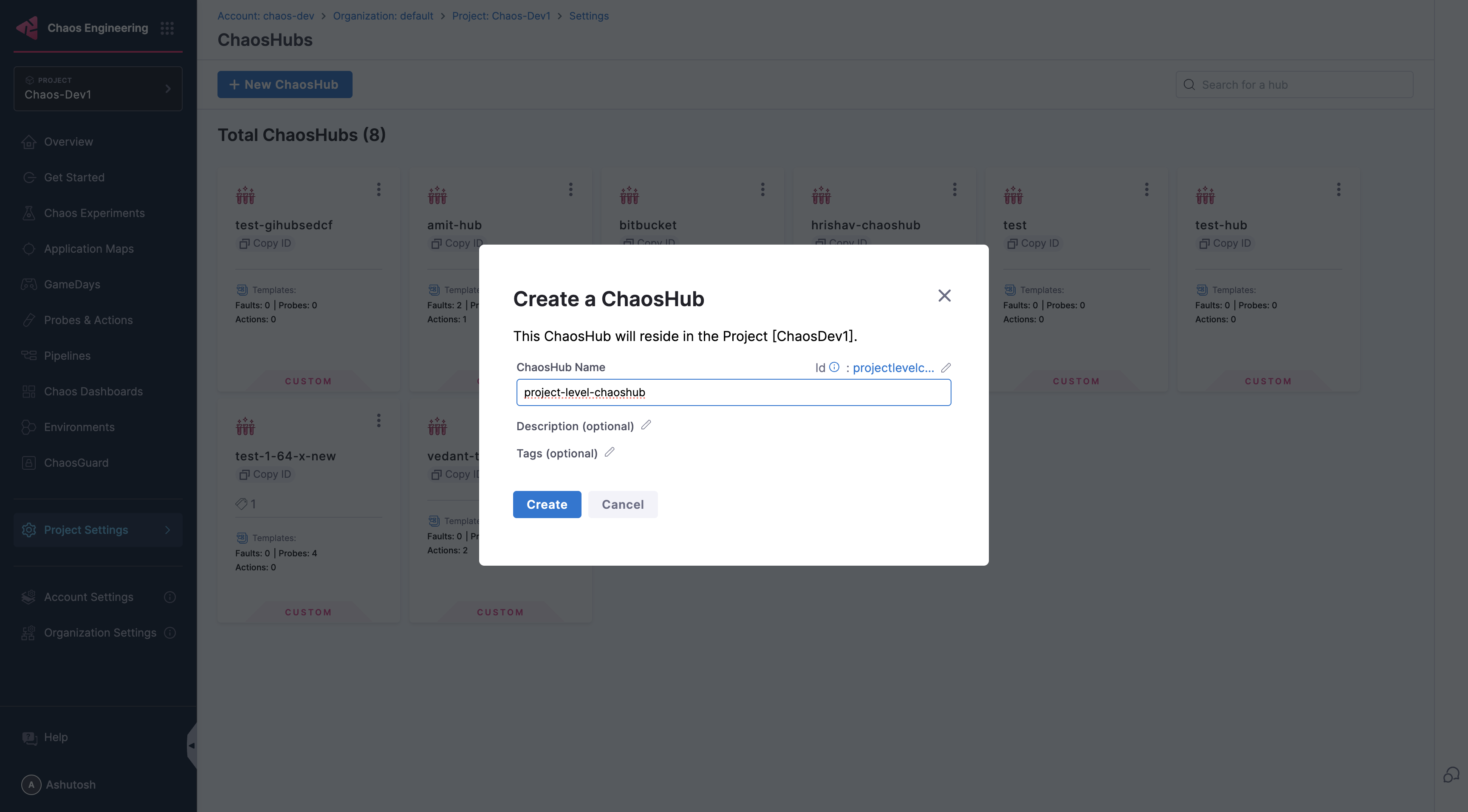
Create a ChaosHub: Click on the ChaosHubs, then click on New ChaosHub, Enter the name of your ChaosHub and click Create
Access Control
ChaosHub access is controlled through Harness RBAC (Role-Based Access Control):
- Account Level: Requires account-level permissions
- Organization Level: Requires organization-level permissions
- Project Level: Requires project-level permissions
Next Steps
- Manage ChaosHub - Understand how to manage existing ChaosHubs
Start with Project-level ChaosHubs for team-specific experiments, then gradually move to Account or Organization level as your chaos engineering practices mature and standardize.